5 Reasons Why The Underside of Your Tongue May Hurt
November 10th, 2016
 We use our tongues to talk, drink, and eat. Any time they get hurt, it can feel like the pain is magnified ten-fold. Usually, pain on the underside of the tongue is caused by a minor injury or ailment and isn’t cause for too much concern. Here are 5 reasons the underside of your tongue may hurt.
We use our tongues to talk, drink, and eat. Any time they get hurt, it can feel like the pain is magnified ten-fold. Usually, pain on the underside of the tongue is caused by a minor injury or ailment and isn’t cause for too much concern. Here are 5 reasons the underside of your tongue may hurt.
#1 - Injury from a Bite
Nearly everyone has accidentally bitten his or her tongue, probably more than once. It can hurt, but the pain usually subsides in a few minutes. Depending on where and how it was bitten, it could hurt more on the underside of the tongue, especially if the bite was the result of a fall or a blow that caused you to bite down inadvertently. Irritation may continue for a few days if your taste buds – the small bumps on the tongue – are injured from the bite and become infected and inflamed.
#2 – Irritation from Foods or Foreign Objects
Common orthodontic devices like dentures and braces can cause tongue pain and irritation if they don’t fit quite right. Often the irritation occurs when someone has just gotten their braces or dentures, and they are still adjusting. Both braces and dentures can cause sores or cuts on the tongue and inside of the mouth that can be remedied by gargling with salt water or using over the counter oral gels or pain relievers.
Irritation can also come from foods, particularly those served at a high temperature like hot cocoa or soup or those that are spicy. Accidentally sipping or biting into something that’s too hot can cause the tongue to feel burned and to become red and swollen. Most tongue burns from too-hot foods are first-degree burns that heal quickly, but more severe burns should be seen and treated by a doctor. Spicy foods can make the tongue feel as if it’s burning and can exacerbate other conditions.
#3 - Canker Sore
Canker sores can develop on the tongue, underneath the tongue, or on the inside of the mouth. The cause is unknown, but they look like a small crater and may be red with white and yellow in the center. Canker sores can be related to irritation and injury from braces or biting the tongue, but may also be triggered by other factors, including stress. They usually stop hurting in 7-10 days and are completely gone within a few weeks.
#4 - Strained Tongue
The tongue is one of the strongest muscles in the body. It’s rare for it to become strained because it’s accustomed to nearly constant use from eating, talking and drinking, but it is possible. A strained tongue would be most likely to occur from overexertion or overuse of the muscle.
#5 – Glossitis, or Inflamed Tongue
Glossitis is inflammation of the tongue that is often the symptom of another issue. Acute glossitis has a sudden onset, usually stemming from an allergic reaction. Chronic glossitis, on the other hand, is recurring and generally signals an underlying health issue. Allergic reactions or irritation from food or medication, low iron levels, mouth trauma, dental appliances like braces or dentures, dry mouth, and certain diseases are all potential causes of different types of glossitis.
There are many reasons people may experience pain on the underside of the tongue Most of them are not serious and will go away within a few days or, at most, a few weeks. Tongue pain, however, can be the sign of a serious underlying medical issue. Always consult with a dentist to ensure that the pain isn’t the result of a severe problem, like a viral infection or even tongue cancer. Reach out to us today to find out what may be causing pain on the underside of your tongue!

 Finding a strange change in your mouth can be scary. You might not know why a mark has appeared, how long it will be there, or what it is. Since it could be a variety of different things, ranging from harmless to more serious, it’s important to visit a dentist or doctor when you find an unfamiliar sore or spot in your mouth.
Finding a strange change in your mouth can be scary. You might not know why a mark has appeared, how long it will be there, or what it is. Since it could be a variety of different things, ranging from harmless to more serious, it’s important to visit a dentist or doctor when you find an unfamiliar sore or spot in your mouth. When it comes to any kind of oral discomfort, there are always many potential reasons for the pain. However, almost always, the pain can be determined as an issue with the teeth, gums, or tongue. When specified to those three, you can narrow down the possible causes of the pain.
When it comes to any kind of oral discomfort, there are always many potential reasons for the pain. However, almost always, the pain can be determined as an issue with the teeth, gums, or tongue. When specified to those three, you can narrow down the possible causes of the pain. When it comes to oral hygiene, Water Tower Dental encourages daily brushing and flossing along with biannual dental cleanings and check ups. Clearing harmful bacteria out of the mouth will help keep your teeth and gums clean and healthy, but what about your breath? Although brushing a flossing can help keep the bacteria that cause bad breath away from your teeth and gums, there's still a chance you'll have bad breath. That's because many of the bacteria can camp out on your tongue. Cue the tongue scraper, a leading tool in keeping harmful bacteria off your tongue.
When it comes to oral hygiene, Water Tower Dental encourages daily brushing and flossing along with biannual dental cleanings and check ups. Clearing harmful bacteria out of the mouth will help keep your teeth and gums clean and healthy, but what about your breath? Although brushing a flossing can help keep the bacteria that cause bad breath away from your teeth and gums, there's still a chance you'll have bad breath. That's because many of the bacteria can camp out on your tongue. Cue the tongue scraper, a leading tool in keeping harmful bacteria off your tongue.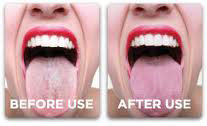 There are several different designs of a tongue scraper (also referred to as a tongue brush or tongue cleaner), but their objective is still the same. Tongue cleaners- unlike toothbrushes- are designed for the purpose of lifting and trapping the plaque coating and removing it from the tongue.
There are several different designs of a tongue scraper (also referred to as a tongue brush or tongue cleaner), but their objective is still the same. Tongue cleaners- unlike toothbrushes- are designed for the purpose of lifting and trapping the plaque coating and removing it from the tongue. A tongue scraper will not just help your bad breath though. A tongue scraper helps remove ama from the tongue. Ama is sanskrit meaning anything that is undigested. Specifically for your mouth, undigested food. Old remnants of food, just like plaque, can build up along the tongue. The more build up you have, however, the less your taste buds can detect flavors of food. By using a tongue scraper, you can actually help your tongue taste food better. That's a great plus for anyone who loves a good meal.
A tongue scraper will not just help your bad breath though. A tongue scraper helps remove ama from the tongue. Ama is sanskrit meaning anything that is undigested. Specifically for your mouth, undigested food. Old remnants of food, just like plaque, can build up along the tongue. The more build up you have, however, the less your taste buds can detect flavors of food. By using a tongue scraper, you can actually help your tongue taste food better. That's a great plus for anyone who loves a good meal.




 Website Powered by Sesame 24-7™
Website Powered by Sesame 24-7™